When it comes to maintaining the health and performance of your Solid State Drive (SSD), formatting is a crucial process. It’s not just about clearing data but about ensuring your Solid State Drive operates at its peak.
Through years of experience and countless interactions with these advanced storage devices, I’ve gathered sufficient knowledge that I’m eager to share with you. With that said, let’s talk about SSD formatting and how to do it right.
Essentials You Should Know About
The SSD Advantage

- Speed and Efficiency: Solid State Drives are renowned for their speed. Unlike traditional hard drives (HDDs), SSDs don’t have moving parts. This means faster access to data and a noticeable boost in performance.
- Durability and Reliability: SSDs are less prone to physical damage. Without spinning disks, your data remains safer from physical shocks, a boon for laptops and mobile devices.
- Silence and Energy Efficiency: Solid State Drives are quiet and consume less power, making them ideal for energy-conscious users and those who prefer a noise-free environment.
Selecting the Right SSD
- Capacity Needs: Assess your storage requirements. For most users, a 256GB to 512GB SSD suffices, balancing cost and space. Gamers and professionals might opt for 1TB or higher.
- Interface and Form Factor: SSDs come in various shapes (2.5-inch, M.2, etc.) and interfaces (SATA, NVMe). Your choice depends on your motherboard’s compatibility and usage purpose.
- Price vs. Performance: Higher-priced SSDs often offer better performance and durability. However, budget-friendly options can still significantly outperform traditional HDDs.
If you’re considering other storage options, such as eMMC, see my comparison in eMMC vs. SSD Storage to make an informed decision.
Pre-Formatting Preparations
- Backup Your Data: Before formatting, back up important data. This cannot be stressed enough. Whether it’s cloud storage or an external drive, ensure your files are safe.
- Gather Necessary Tools: You’ll need a screwdriver for physical installation and software tools for the formatting process.
- Know Your System: Understand your computer’s specifications. This helps in choosing the right SSD and the formatting method.
The Formatting Process: Step-by-Step
Installation
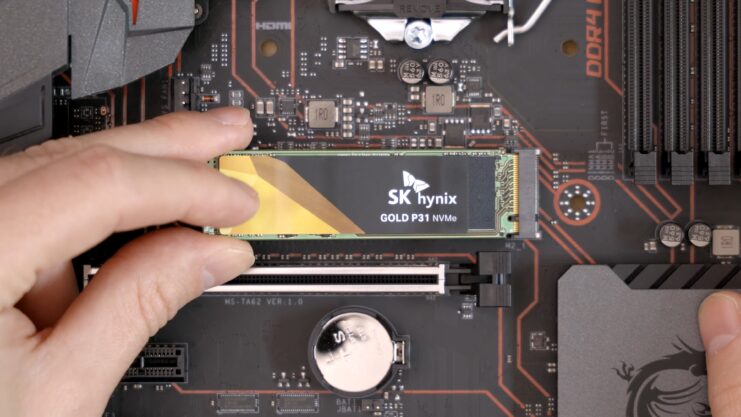

- Physical Installation: Carefully install the SSD into your computer. For laptops, this usually involves unscrewing the back panel. Desktops may require mounting the SSD onto a drive bay.
- Connecting the SSD: Ensure the Solid State Drive is properly connected to the motherboard. For SATA Solid State Drives, this involves a SATA cable and a power cable. M.2 SSDs slot directly onto the motherboard.
- Booting Up: Power on your computer. It should recognize the new SSD. If not, check the connections and BIOS settings.
Formatting Process
- Access Disk Management: On Windows, open Disk Management. For Macs, use Disk Utility. These tools allow you to format and partition your SSD.
- Partitioning the SSD: Create a new partition. This process involves defining the usable space on your SSD. For most users, a single partition is sufficient.
- Choosing the Right File System: Select a file system. NTFS is standard for Windows, while MacOS prefers APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Linux users might choose Ext4.
Post-Formatting Setup
- Installing the Operating System: If your SSD is the primary drive, install your operating system. Use a bootable USB drive or installation disc.
- Driver Updates and Optimization: After installation, update your drivers and optimize settings for SSD use. This includes enabling features like TRIM for maintaining SSD performance.
- Restoring Your Data: With your system up and running, restore your backed-up data to your newly formatted SSD.
Keeping Your SSD in Top Shape
Regular Maintenance Tips
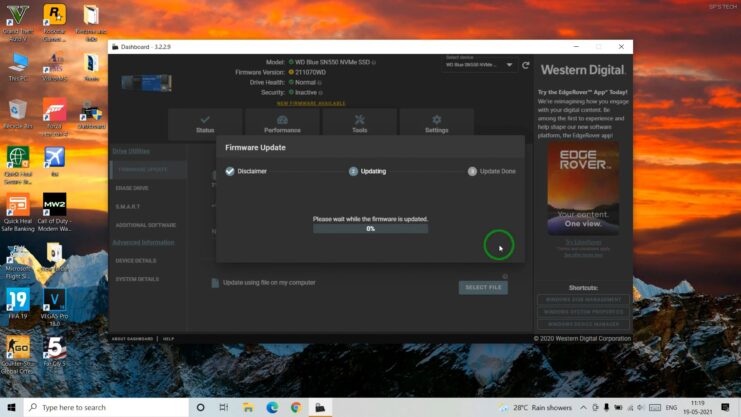
- Keep Your Firmware Updated: Manufacturers release firmware updates that can improve performance and fix bugs.
- Avoid Unnecessary Writes: Solid State Drives have a limited number of write cycles. Minimize unnecessary data writing to prolong its lifespan.
- Monitor Drive’s Health: Use SSD monitoring tools to keep an eye on its health and performance metrics.
Optimizing Performance
- Enable TRIM: This command helps the Solid State Drive efficiently manage unused data, maintaining optimal performance.
- Disable Disk Defragmentation: Unlike HDDs, Solid State Drives don’t benefit from defragmentation and it can actually reduce their lifespan.
- Adjust Power Settings: Ensure your power settings don’t put the SSD into a low-power state, which can impact performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Detection Problems: If your Solid State Drive isn’t detected, check the connections and BIOS settings.
- Slow Performance: This could be due to outdated firmware or incorrect settings. Ensure TRIM is enabled and the Solid State Drive is operating in AHCI mode.
- Capacity Issues: If your Solid State Drive shows incorrect capacity, it might need a firmware update or reformatting.
Advanced Tips

Over-provisioning for Enhanced Performance
- What is Over-Provisioning?: Allocating extra, unpartitioned space on your SSD. This space isn’t used for storage but helps in wear leveling and performance.
- Benefits: Over-provisioning can extend the lifespan of your SSD and maintain its performance over time.
- How to Over-Provision: Use your SSD’s software tool to allocate over-provisioning space. Around 10% of the drive’s capacity is a good benchmark.
Upgrading Firmware: A Crucial Step
- Why Upgrade Firmware: Firmware updates can improve performance, fix bugs, and add new features.
- Safety First: Ensure your data is backed up before a firmware update to prevent data loss in case of an error.
- Following Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for firmware updates to avoid issues.
Encrypting for Security
- Why Encrypt: To protect sensitive data. If your laptop is stolen, encryption keeps your data safe.
- Using Built-In Tools: Many operating systems offer built-in encryption tools like BitLocker for Windows or FileVault for MacOS.
- Performance Considerations: While encryption can slightly reduce performance, modern Solid State Drives handle encryption efficiently.
Future Outlook
Emerging Technologies
- NVMe Over Fabrics (NVMe-oF): This technology extends the benefits of NVMe Solid State Drives across a network. It’s poised to revolutionize data centers by enabling faster and more efficient access to storage over long distances.
- QLC NAND: Quad-Level Cell (QLC) technology stores four bits per cell, increasing storage density. It’s ideal for read-heavy applications and can bring larger-capacity Solid State Drives to the mainstream market.
- 3D XPoint and Optane: Intel’s 3D XPoint, used in Optane SSDs, offers significantly faster read/write speeds and higher endurance than traditional NAND SSDs. It’s paving the way for new high-performance computing applications.
The Future of SSDs in Consumer Electronics
- Widespread Adoption in Devices: As prices continue to drop, expect Solid State Drives to become standard in most consumer electronics, including budget laptops, tablets, and even smartphones.
- Gaming Consoles: The latest gaming consoles have already embraced SSDs for faster game loading times. This trend is likely to continue, enhancing the gaming experience.
- Portable SSDs: External SSDs are becoming popular for their speed and portability, offering a quick way to transport large amounts of data.
FAQs
Can I format an SSD from the BIOS?
No, you cannot. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is used primarily for hardware initialization and does not have the capability to format storage devices.
To format a Solid State Drive, you need to use an operating system-based utility like Disk Management in Windows or Disk Utility in macOS.
Is it necessary to defragment an SSD?
No, it is not necessary and is actually not recommended to defragment a Solid State Drive. SSDs access memory randomly, unlike HDDs, which store data sequentially.
Defragmentation is beneficial for HDDs because it minimizes the physical movement of the read/write head. Since Solid State Drives have no moving parts, defragmentation does not improve performance and can reduce the lifespan of the SSD by causing unnecessary write operations.
Can a virus survive an SSD format?
In most cases, a full format of a Solid State Drive will remove viruses. However, some sophisticated malware can reside in the firmware or the master boot record (MBR), surviving a standard format.
To completely remove such viruses, a more thorough method, like a secure erase command that resets the SSD to factory settings, might be necessary.
Does formatting an SSD improve its performance?
Formatting doesn’t directly improve its performance. However, formatting can help in cases where the file system is corrupted, causing performance issues.
In such cases, formatting and reinstalling the operating system can restore the Solid State Drive to its optimal performance.
How often should I format my SSD?
Regular formatting is not necessary and is not recommended. Unlike HDDs, Solid State Drives have limited write cycles, and frequent formatting can reduce their lifespan.
Formatting should only be done when necessary, such as when installing a new operating system or if there are significant issues with the drive.
Can formatting fix a failing SSD?
Formatting cannot fix physical damage or wear-related failures. If a Solid State Drive is failing due to bad sectors or wear and tear, formatting will not restore its functionality.
In such cases, it’s best to replace it to ensure data integrity and system stability.
Concluding Thoughts
By following these steps, you’ll have an SSD that’s not only correctly formatted but also optimized for longevity and performance. A Solid State Drive isn’t just a purchase but an investment in the efficiency and speed of your computing experience.
With the right care, it’s an investment that pays off handsomely, making your computer faster, more reliable, and more enjoyable to use. Remember, the key to maximizing a Solid State Drive’s potential lies in understanding its capabilities and treating it with the respect it deserves.
With this guide, you’re well on your way to experiencing the full spectrum of benefits an SSD has to offer.

