Understanding the distinction between a proxy and a VPN is key to navigating the online world safely and privately. While both offer protection, they function uniquely and provide varying degrees of security. Let’s break down these technologies to help you make an informed choice for your online needs.
The Basics Explained
Proxy: The Mask for Your IP
A proxy server acts as a go-between for your computer and the internet. It uses its IP address to request web pages on your behalf.
When you surf the internet, the proxy handles your requests and fetches the pages for you. It’s useful for anonymous browsing or bypassing regional restrictions, but keep in mind, it doesn’t encrypt your data, making it less suitable for confidential tasks.
VPN: The Secure Tunnel
A VPN creates a secure bridge over a public network, encrypting your data as if your devices were linked directly to a private network. This comprehensive security covers your whole internet connection, not just browser activity, making VPNs ideal for protecting sensitive information, particularly on public Wi-Fi.
For an in-depth analysis of how businesses can effectively utilize these tools, explore the insights shared by nordlayer.com, where they delve into the practical applications of VPNs and proxies in corporate environments.
Key Differences Between Proxy and VPN
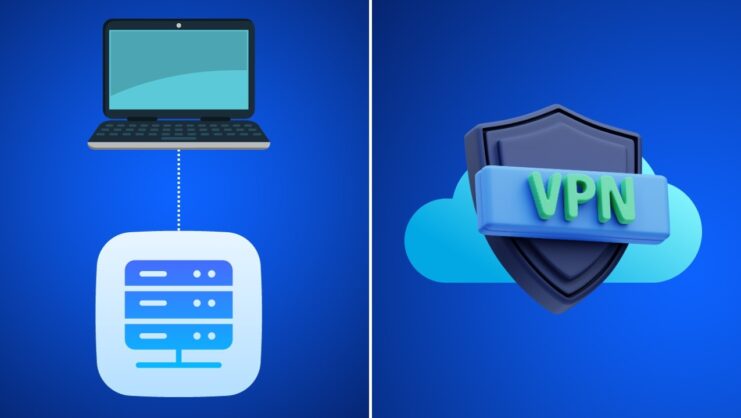

Privacy and Security
- Proxy: Provides a basic level of anonymity by hiding your IP address. However, since it doesn’t encrypt your data, your online activities can still be tracked or intercepted.
- VPN: Offers a higher level of security. It not only hides your IP address but also encrypts your data. This makes it almost impossible for anyone to track your online activities or steal your data.
Performance and Speed
- Proxy: Generally faster than a VPN because it doesn’t encrypt your data. This makes it suitable for simple tasks like streaming geo-restricted content.
- VPN: Might slow down your connection due to the encryption process. However, modern VPNs have optimized their speed, minimizing the impact.
Use Cases
- Proxy: Ideal for bypassing content restrictions or anonymous browsing. It’s a good choice for tasks that don’t involve sensitive data.
- VPN: Best for securing data on public Wi-Fi, accessing sensitive information, and maintaining privacy in various online activities.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs

When to Use a Proxy
- When you need to quickly bypass geo-restrictions.
- For simple tasks like watching region-blocked videos.
- When you don’t need to encrypt your data.
When to Use a VPN
- For securing data on public Wi-Fi networks.
- When accessing sensitive information like bank accounts.
- For comprehensive privacy protection.
Delving Deeper: Technical Aspects
How Proxies Work
Proxies essentially reroute your online requests via another server. This process changes your IP address, giving the impression that you’re browsing from a different place. There are different kinds of proxies available:
- HTTP Proxies: Handle web traffic and are suitable for browsing.
- SOCKS Proxies: More versatile and can handle all types of internet traffic, but slower.
- Transparent Proxies: Automatically direct your traffic without manual configuration, often used in businesses and schools for content filtering and monitoring.
How VPNs Function
VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. Your data travels through this tunnel, encrypted, keeping it secure from external threats. Key components of VPNs include:
- Encryption Protocols: Tools like OpenVPN, WireGuard, and IPSec encrypt your data, ensuring its security.
- Tunneling Protocols: Explore how VPNs send data. Protocols like PPTP, L2TP, and SSTP differ in speed and security.
- Servers: VPN providers have servers worldwide, allowing you to choose where your encrypted data emerges on the internet.
Proxy Pros and Cons

Pros
- Quick setup and easy to use.
- Suitable for lightweight tasks like streaming and browsing.
- Often free or low-cost.
Cons
- Doesn’t encrypt data, making it less secure.
- Only reroutes traffic from your browser or specific apps.
- Free proxies can be unreliable and slow.
VPN Pros and Cons
Pros
- Provides end-to-end encryption for all internet traffic.
- Hides your IP address and encrypts data, offering superior privacy and security.
- Bypasses geo-restrictions and censorship more effectively.
Cons
- Typically slower than proxies due to encryption.
- Can be more expensive than proxies.
- Requires software installation and configuration.
Real-World Applications

Proxies in Action
- Content Access: Proxies are used to access region-specific content on streaming platforms like Netflix or YouTube.
- Market Research: Businesses use proxies to see their websites from different geographic locations, understanding how they appear in various markets.
VPNs in the Real World
- Secure Remote Work: VPNs enable secure access to company networks for remote workers, protecting sensitive corporate data.
- Privacy Advocacy: Activists and journalists in oppressive regimes use VPNs to bypass censorship and communicate securely.
Future Trends

The Evolution of Proxies and VPNs
- Improved Security: With increasing cyber threats, both proxies and VPNs are evolving to offer better security features.
- Speed and Efficiency: VPN providers are focusing on overcoming speed limitations through new technologies like WireGuard.
- Regulatory Challenges: VPNs face challenges with governments imposing regulations, which might change how they operate.
Final Words
Both proxies and VPNs are essential tools in the digital age, each serving specific purposes. A proxy is suitable for basic, non-sensitive tasks, while a VPN offers comprehensive security and privacy. Your choice between a proxy and a VPN should be guided by your specific needs, be it simple anonymous browsing or robust data encryption.
Understanding the distinct roles of these technologies ensures you’re equipped with the right tool to navigate the digital world securely and privately. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions to protect your online presence effectively.

