Navigating the intricacies of APA (American Psychological Association) citation style can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to citing theses and dissertations.
This comprehensive guide aims to simplify the process, ensuring that your academic work adheres to the highest standards of accuracy and integrity. It doesn’t matter if you’re a seasoned scholar or a budding researcher; mastering APA thesis citations is crucial for your academic journey.
The Basics of APA Formatting
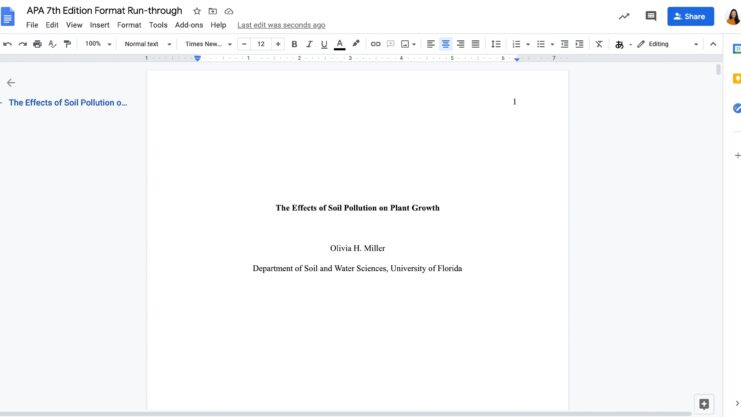
APA style is not just a way of formatting citations but a comprehensive system for writing scholarly papers.
It encompasses everything from the layout of the page to the way sources are cited. The style is designed to promote clarity, precision, and a professional presentation of information.
- Consistency: APA style provides a uniform framework for consistency across a wide range of disciplines. This consistency makes it easier for readers to understand the structure and find referenced materials.
- Credibility: Proper citation enhances the credibility of your work. It shows that you have engaged with relevant literature and provides a pathway for readers to follow your research journey.
For expert assistance in ensuring your thesis adheres to APA citation guidelines, consider professional services such as thesisrush.com, where specialized guidance is available for academic writing.
The Role of Citations in Academic Writing
Citations are not just a formality; they are a critical part of academic writing. They serve several key purposes:
- Acknowledging Sources: Citations give credit to the authors whose work you have used in your research.
- Supporting Arguments: They provide evidence for the claims and arguments you make in your paper.
- Avoiding Plagiarism: Proper citation is essential for avoiding plagiarism, a serious academic offense.
General Format for Thesis Citations

When citing a thesis or dissertation, the APA format includes several key pieces of information:
- Author: The name of the thesis author.
- Date: The year of publication.
- Title: The title of the thesis, in italics.
- University: The name of the institution where the thesis was submitted.
- Degree: Indication of the type of thesis (e.g., Doctoral dissertation or Master’s thesis).
Examples
For an Unpublished Thesis
- Smith, J. (2020). Exploring Behavioral Patterns in Non-Verbal Communication (Unpublished master’s thesis). University of California, Berkeley.
For a Published Thesis
- Doe, J. (2018). A Study of Emotional Intelligence (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database. (UMI No. 123456)
Special Considerations
- Electronic Theses: If the thesis is retrieved from a database, include the name of the database and the accession or order number.
- URLs: For theses retrieved from a university repository, include the URL at the end of the citation.
Advanced Tips

Managing Citations in Long Documents
In longer academic works, managing citations can become complex. Here are some tips to keep track:
- Use Citation Management Software: Tools like Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley can be invaluable.
- Consistent Formatting: Ensure that all your citations follow the same APA format.
- Regularly Update Your References: As your research progresses, keep your reference list updated.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced writers can make mistakes. Here are some to watch out for:
- Inconsistent Formatting: This can confuse readers and detract from the professionalism of your paper.
- Incorrect Author or Date: Always double-check these details.
- Forgetting the URL or Database Information: This is crucial for electronic sources.
Maneuvering Complex Citation Scenarios

Citing a Thesis With Multiple Authors
In cases where a thesis has multiple authors, the citation format changes slightly:
- Two Authors: List both authors in the order they appear on the document. For example: Johnson, A., & Smith, B. (2019).
- Three or More Authors: List the first author followed by et al. For example: Taylor, L. et al. (2021).
Translated Theses
If you are citing a thesis that has been translated, include the original language in brackets after the title:
- Example: Nguyen, P. (2017). Studies on Bacterial Resistance in Aquatic Environments [Translated from Vietnamese]. University of Science, Vietnam.
Citing a Section or Chapter of a Thesis
Sometimes, you may need to cite a specific section or chapter of a thesis:
- Example: Lee, C. (2018). The Role of Genetics in Modern Medicine (Doctoral dissertation, Harvard University). In Genetic Markers in Oncology (Chapter 3).
Leveraging Technology for Accurate Citations

Citation generators can be a useful tool, especially for students and researchers juggling multiple sources. However, it’s important to:
- Double-Check the Output: Ensure that the generated citation adheres to APA guidelines.
- Understand the Basics: Knowing the fundamentals of APA citation will help you spot any errors a generator might make.
Incorporating Citations in Digital Documents
Modern word processors have built-in features to manage citations. These tools can:
- Automatically Format Citations: They can format your citations according to APA style.
- Manage Your Bibliography: They keep track of all your cited works and format them correctly.
Best Practices for APA Thesis Citations

Consistency is Key
Ensure that every citation in your document follows the same APA format. This consistency aids in readability and professionalism.
Proofreading
Always double-check your citations for accuracy. Pay special attention to author names, publication dates, and titles.
Use Primary Sources
Whenever possible, cite primary sources to ensure that your references are as accurate and authoritative as possible.
Stay Informed
Keep up-to-date with the latest editions of the APA Publication Manual, as citation guidelines can change.
Tables and Figures in APA Style

Incorporating Tables
When including tables in your document:
- Number Tables Consecutively: Tables should be numbered in the order they are mentioned in the text.
- Provide a Title: Each table should have a clear, concise title that explains its contents.
- Note Source: If the table is from another source, cite the source beneath the table.
Using Figures
For figures:
- Number Figures Sequentially: Like tables, figures should be numbered in the order they appear in the text.
- Include a Caption: Provide a caption that explains the figure.
- Cite the Source: If the figure is not your own, cite the source below the figure.
Closing Thoughts
Mastering APA thesis citations is a vital skill for any academic writer. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your citations are accurate, complete, and in line with APA standards.
Remember, proper citation is not just about avoiding plagiarism; it’s about contributing to a scholarly conversation with respect and integrity. As you continue your academic journey, let these principles guide your path to success.

